南大 – 软件分析
Introduction
编程语言的分类
指令式编程(Imperative programming)
声明式编程(Declarative programming)
逻辑式编程(Logic programming)
函数式编程(Functional programming)
约束编程(Constraint programming)
静态分析的作用
- Program Reliability: 程序可靠性
- Null pointer dereference: 空指针解引用
- Memory leak: 内存泄漏
- Program Security: 程序安全性
- Private information leak: 私有信息泄露
- Injection attack: 注入攻击
- Compiler Optimization: 编译器优化
- Dead code elimination: 死代码消除
- Code motion: 代码移动
- Program Understanding: 程序理解
- IDE call hierarchy: IDE(集成开发环境)调用层次结构
- Type indication: 类型指示
静态分析的定义
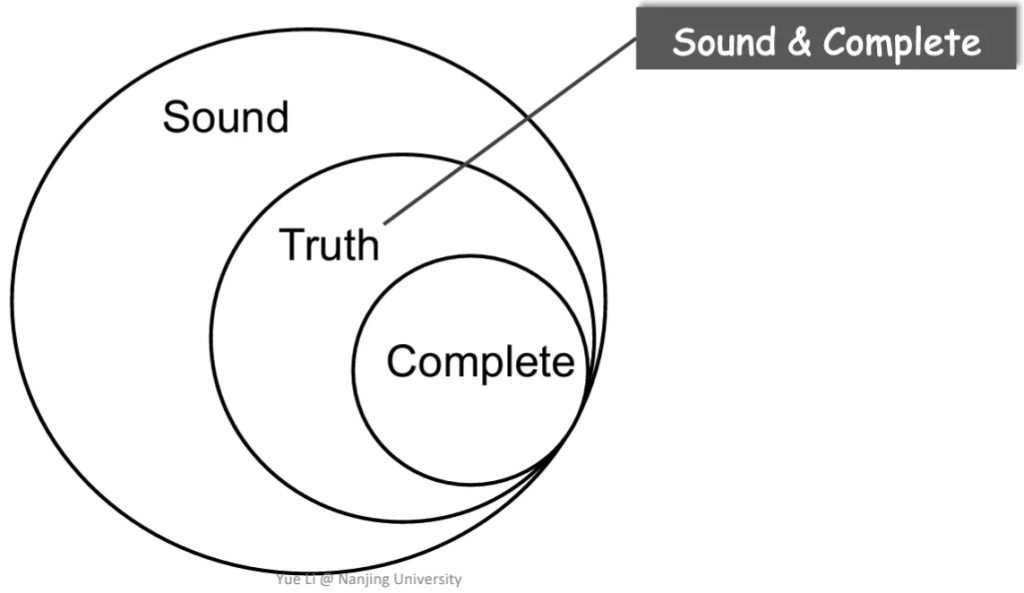
Static Analysis: ensure (or get close to) soundness, while makinggood trade-offs between analysis precision and analysis speed.
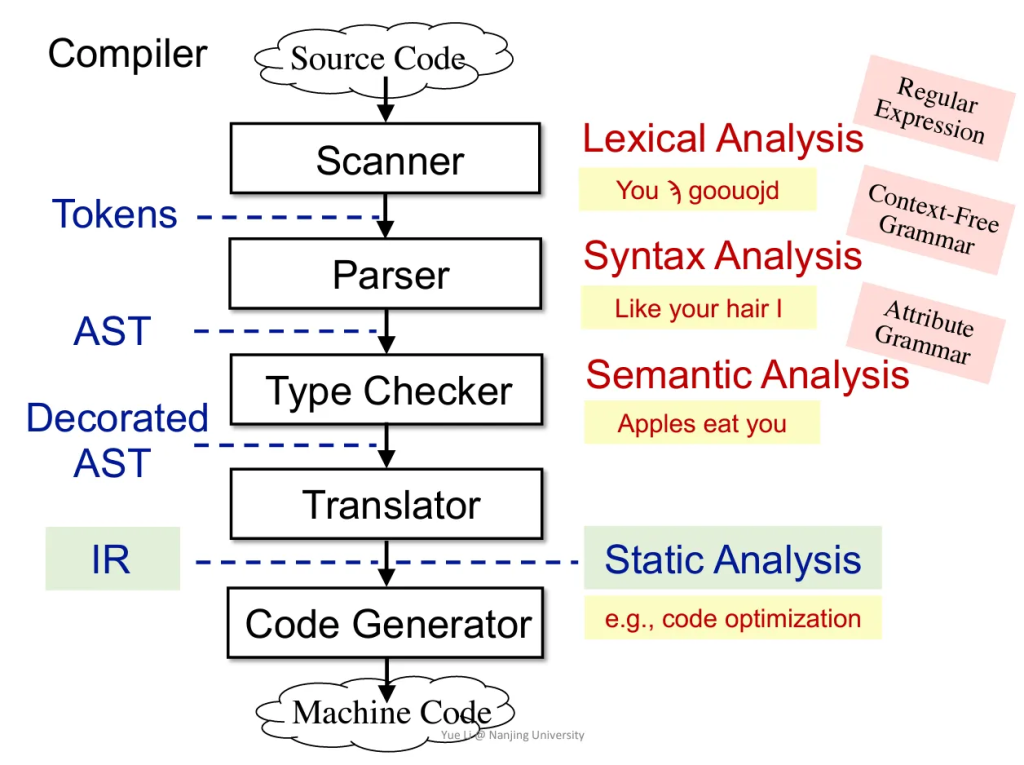
Intermediate Representation